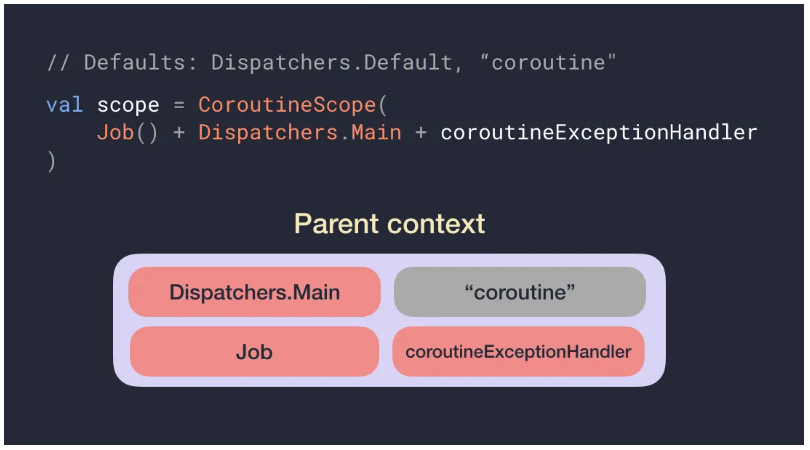
코루틴 컨텍스트(Coroutine Context)란?
CoroutineContext는 코루틴을 실행하는 실행 환경을 설정하고 관리하는 인터페이스로,
CoroutineContext 객체는 CoroutineDispatcher, CoroutineName, Job 등의 객체를 조합하여 코루틴의 실행 환경을 설정합니다.
따라서, CoroutineContext 객체는 코루틴 실행 및 관리의 핵심 역할을 합니다.
CoroutineContext는 launch나 async 코루틴 빌더의 파라미터로 설정할 수 있으며, 해당 파라미터에 CoroutineContext를 명시적으로 지정하면 특정 스레드풀로 수행 제한, 코루틴 이름 설정 등을 할 수 있습니다.
CoroutineContext 구성 요소
- CoroutineDispatcher
- 코루틴 실행 시, 어떤 스레드에서 수행(특정 스레드로 수행 제한, 특정 스레드 풀에서 실행하도록 함)할지 결정합니다.
- CoroutineName
- 코루틴의 이름을 설정합니다. 디버깅할 때 유용함
- CoroutineExceptionHandler
- 코루틴에서 발생한 예외처리를 결정합니다.
- Job
- 코루틴에 대한 핸들러입니다. launch 또는 async에 의해 생성된 모든 코루틴에 대해 코루틴을 식별하고, 코루틴의 라이프 사이클을 관리합니다.
그렇다면 CoroutineContext는 어떤 코드로 구성되어 있을까요?
구현 코드를 살펴보겠습니다.
public interface CoroutineContext {
/**
* Returns the element with the given [key] from this context or `null`.
* Keys are compared _by reference_, that is to get an element from the context the reference to its actual key
* object must be presented to this function.
*/
public operator fun <E : Element> get(key: Key<E>): E?
/**
* Accumulates entries of this context starting with [initial] value and applying [operation]
* from left to right to current accumulator value and each element of this context.
*/
public fun <R> fold(initial: R, operation: (R, Element) -> R): R
/**
* Returns a context containing elements from this context and elements from other [context].
* The elements from this context with the same key as in the other one are dropped.
*/
public operator fun plus(context: CoroutineContext): CoroutineContext = ...impl...
/**
* Returns a context containing elements from this context, but without an element with
* the specified [key]. Keys are compared _by reference_, that is to remove an element from the context
* the reference to its actual key object must be presented to this function.
*/
public fun minusKey(key: Key<*>): CoroutineContext
}
/**
* Key for the elements of [CoroutineContext]. [E] is a type of element with this key.
* Keys in the context are compared _by reference_.
*/
public interface Key<E : Element>
/**
* An element of the [CoroutineContext]. An element of the coroutine context is a singleton context by itself.
*/
public interface Element : CoroutineContext {
/**
* A key of this coroutine context element.
*/
public val key: Key<*>
...overrides...
}
위 코드는 CoroutineContext.kt 파일에 있는 코드 입니다. CoroutineContext 는 4가지 메서드를 가지고 있는데 그 역할은 다음과 같습니다.
1. get() : 연산자(operator) 함수로써 주어진 key 에 해당하는 컨텍스트 요소를 반환합니다.
fun main() {
val exceptionHandler = CoroutineExceptionHandler { _, throwable ->
println("예외 발생: ${throwable.message}")
}
val context: CoroutineContext = Dispatchers.IO + CoroutineName("ExampleCoroutine") + Job() + exceptionHandler
//이름 요소 가져오기
val coroutineName = context[CoroutineName] // 특정 키를 가진 요소 가져오기
println("코루틴 이름: ${coroutineName?.name}") // 코루틴 이름 출력
//job 요소 가져오기
val job = context[Job] // Job 요소 가져오기
println("Job 상태: ${job?.isActive}") // Job이 활성 상태인지 확인
//디스패쳐 가져오기
val dispatcher = context[CoroutineDispatcher] // 디스패처 가져오기
println("코루틴 디스패처: $dispatcher")
//CoroutineExceptionHandler 가져오기
val handler = context[CoroutineExceptionHandler] // 예외 처리 핸들러 가져오기
println("CoroutineExceptionHandler 존재 여부: ${handler != null}")
}
//코루틴 이름: ExampleCoroutine
//Job 상태: true
//코루틴 디스패처: kotlinx.coroutines.scheduling.IOParallelDispatcher@xxxxxxxx
//CoroutineExceptionHandler 존재 여부: true
2. fold() : 초기값(initialValue)을 시작으로 제공된 병합 함수를 이용하여 대상 컨텍스트 요소들을 병합한 후 결과를 반환합니다.
예를들어 초기값을 0을 주고 특정 컨텍스트 요소들만 찾는 병합 함수(filter 역할)를 주면 찾은 개수를 반환할 수 있고,
초기값을 EmptyCoroutineContext 를 주고 특정 컨텍스트 요소들만 찾아 추가하는 함수를 주면 해당 요소들만드로 구성된 코루틴 컨텍스트를 만들 수 있습니다.
fun main() {
val context: CoroutineContext = Dispatchers.IO + CoroutineName("ExampleCoroutine") + Job()
val count = context.fold(0) { acc, _ -> acc + 1 } // 요소 개수 카운트
println("컨텍스트 요소 개수: $count")
}
//컨텍스트 요소 개수: 3fun main() {
val context: CoroutineContext =
Dispatchers.Default + CoroutineName("FilteredCoroutine") + Job()
// CoroutineName 요소만 포함된 새로운 컨텍스트 만들기
val filteredContext = context.fold(EmptyCoroutineContext) { acc, element ->
if (element is CoroutineName) acc + element else acc
}
println("필터링된 컨텍스트: ${filteredContext[CoroutineName]}")
}
//필터링된 컨텍스트: CoroutineName(FilteredCoroutine)
3. plus() : 현재 컨텍스트와 파라미터로 주어진 다른 컨텍스트가 갖는 요소들을 모두 포함하는 컨텍스트를 반환합니다. 현재 컨텍스트 요소 중 파라미터로 주어진 요소에 이미 존재하는 요소(중복)는 버려집니다.
fun main() {
val mergedContext1: CoroutineContext = Dispatchers.IO + CoroutineName("FirstCoroutine")
val mergedContext2: CoroutineContext = Job() + CoroutineName("SecondCoroutine")
val mergedContext3 = mergedContext1 + mergedContext2 // 두 컨텍스트 합치기
println("코루틴 이름1: ${mergedContext1[CoroutineName]?.name}")
println("코루틴 이름2: ${mergedContext2[CoroutineName]?.name}")
println("코루틴 이름3: ${mergedContext3[CoroutineName]?.name}")
}
//코루틴 이름1: FirstCoroutine
//코루틴 이름2: SecondCoroutine
//코루틴 이름3: SecondCoroutine
4. minusKey() : 현재 컨텍스트에서 주어진 키를 갖는 요소들을 제외한 새로운 컨텍스트를 반환합니다.
fun main() {
val context: CoroutineContext = Dispatchers.IO + CoroutineName("ExampleCoroutine") + Job()
val newContext = context.minusKey(CoroutineName) // CoroutineName 제거
println("제거 후 CoroutineName 존재 여부: ${newContext[CoroutineName]}")
}
//제거 후 CoroutineName 존재 여부: null
그리고 CoroutineContext에서는 Key 에 대한 인터페이스 정의가 있는데 Key 는 Element 타입을 제네릭 타입으로 가져야 합니다.
여기서 Element는 CoroutineContext를 상속하며 CoroutineId, Job, CoroutineName, CroutineDispatcher, CorotuineExceptionHandler 등을 들 수 있습니다.
이런 요소(element)들은 각각의 Key를 기반으로 CoroutineContext에 등록됩니다.
요약하자면 코루틴 컨텍스트(CoroutineContext)에는 코루틴 컨텍스트를 상속한 요소(Element) 들이 등록될 수 있고, 각 요소들이 등록 될때는 요소의 고유한 키를 기반으로 등록된다는 것입니다.
CoroutineContext 는 인터페이스로써 이를 구현한 구현체로는 다음과같은 3가지 종류가 있습니다.
- EmptyCoroutineContext: 특별히 컨텍스트가 명시되지 않을 경우 이 singleton 객체가 사용됩니다.
이는 GlobalScope에 사용된 Context로, GlobalScope == launc{ }는 같은 싱글톤 EmptyContext를 사용하는 의미입니다. - CombinedContext: 두개 이상의 컨텍스트가 명시되면 컨텍스트 간 연결을 위한 컨테이너역할을 하는 컨텍스트 입니다.
* 명시란? - launch(Dispatchers.Main + job) 이렇게 코루틴 생성 시 프로퍼티를 설정한다는 의미 - Element: 컨텍트스의 각 요소들도 CoroutineContext 를 구현합니다.
* launch(), launch(Dispatcher.IO), launch(CoroutineName("example)) 등이 있습니다.
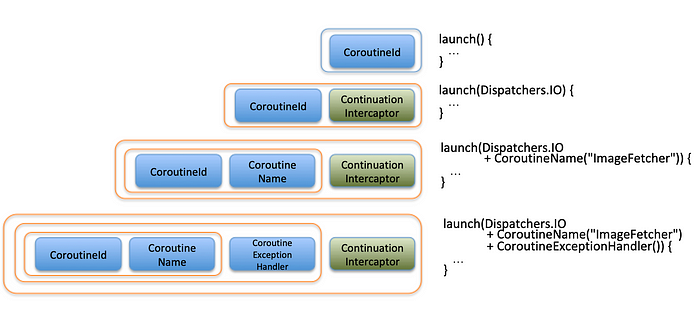
위 이미지는 우리가 GlobalScope.launch{} 를 수행할 때 launch 함수의 첫번째 파라미터인 CoroutineContext 에 어떤 값을 넘기는지에 따라서 변화되어 가는 코루틴 컨텍스트의 상태를 보여줍니다.
각각의 요소를 + 연산자를 이용해 연결하고 있는데 이는 앞서 설명한 것처럼CoroutineContext 가 plus 연산자를 구현하고 있기 때문입니다. Element + Element + … 는 결국 하나로 병합 된 CoroutineContext (e.g. CombinedContext)를 만들어냅니다.
주황색 테두리는 CombinedContext 로서 CoroutineContext 와 Element 를 묶어 하나의 CoroutineContext 가 되는 개념입니다. 그리고 내부 코드에서 ContinuationInterceptor 는 이 병합 작업이 일어날 때 항상 마지막에 위치하도록 고정되는데 이는 인터셉터로의 빠른 접근을 위해서라고 커멘트 되어 있습니다.
참고자료
https://earth-95.tistory.com/m/198
[Kotlin Coroutine] 코루틴 컨텍스트와 디스패처의 이해
목표코루틴 컨텍스트와 디스패처의 역할 및 중요성 학습다양한 디스패처(Main, IO, Default) 사용 시나리오 실습컨텍스트 전환과 예외 처리 방법 탐구CoroutineContextcoroutineContext는 코루틴을 실행하는
earth-95.tistory.com
https://android-devpia.tistory.com/10
코틀린 코루틴에서의 취소 및 예외 처리 #1 - CoroutineScope, Job, CoroutineContext
이 포스팅은 아래 게시글을 번역 및 일부 수정하여 작성하였습니다. https://medium.com/androiddevelopers/coroutines-first-things-first-e6187bf3bb21 이 일련의 포스팅은 코루틴의 취소와 예외에 대하여 자세히 설
android-devpia.tistory.com
https://myungpyo.medium.com/reading-coroutine-official-guide-thoroughly-part-1-7ebb70a51910
코루틴 공식 가이드 읽고 분석하기- Part 1 — Dive1
CoroutineContext와 CoroutineScope 란 무엇인가?
myungpyo.medium.com
https://jaejong.tistory.com/62
[Kotlin] 코루틴 #2 - CoroutineContext와 CoroutineScope란?
코루틴 #2 - CoroutineContext와 CoroutineScope란? CoroutineContext와 CoroutineScope란 무엇인가? Coroutine 이전 글 코루틴 #1 - 기본 CoroutineContext Coroutine(코루틴)을 어떻게 처리할 것인지에 대한 여러가지 정보(Elemen
jaejong.tistory.com
'Android > Coroutine' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Android] 코루틴(Coroutine) 예외 처리 방법 (1) | 2024.11.09 |
|---|---|
| [Android] 코루틴(Coroutine)의 구조적 동시성(Structured Concurrency) (0) | 2024.11.09 |
| [Android] 코루틴(Coroutine) Builder에 대한 고찰 - Deep Dive (0) | 2024.11.09 |
| [Android] 코루틴(Coroutine) Scope에 대한 고찰 - Deep Dive (0) | 2024.11.09 |
| [Android] 코루틴(Coroutine)의 개념 (1) | 2024.11.08 |